What is Self-Custody in Crypto? A Complete Beginner's Guide
Learn what self-custody means, why it matters, and how to secure your crypto with real-time protection. Your keys, your coins.

Key Takeaways
- Self-custody means you control your private keys and truly own your crypto - no exchange can freeze, lose, or mismanage your funds like FTX and Mt. Gox did.
- Your seed phrase and private key are the most important things to protect - write it on paper, store it securely, and never photograph, digitize, or share it with anyone.
- Phishing and social engineering remain the biggest threats to self-custody users, since scammers trick people into handing over access rather than hacking wallets directly.
Introduction
In November 2022, FTX, once the world’s third-largest crypto exchange, collapsed within days after rumors of fraud and user funds mismanagement became fact. Over one million customers suddenly lost access to their funds, with an $8 billion hole discovered in the company’s accounts.
While many users eventually received compensation, they’d been locked out of their assets for nearly 24 months during a period when Bitcoin prices surged 290%.
FTX’s demise was one of several custodial shocks in 2022, which together with the Luna Terra collapse caused others like 3 Arrows Capital, Celsius, BlockFi and Voyager to also keel over.
More recently, in February 2025, the Bybit exchange suffered the largest crypto theft in history when hackers stole $1.4 billion in Ethereum.
Of course, it’s not only crypto. Who can forget the 2008 financial crisis, which saw TradFi giants like Lehman Brothers and Bear Stearns fall in mere days (and inspired the creation of Bitcoin)?
These incidents should force every Web3 user to ask their most important question:
Who actually controls my crypto?
If the World Economic Forum has their way, in the future you’ll own nothing and be happy. If you reject that hellish forecast, then you’re in luck. Crypto solves this.
It’s called self-custody, and it’s easier than you think.
Crypto was created to remove the need for bloated financial intermediaries, the very thing that centralized exchanges (CEXs) and ETFs reintroduced. While these tools provide many benefits, they still come with third-party risk.
This guide breaks down what self-custody actually means, why it matters, and how to do it without losing your shirt (or your sanity).
Understanding Self-Custody: The Basics
What Self-Custody Actually Means
No, self-custody doesn’t mean to look after yourself. Rather, it refers to you holding the private keys to your cryptocurrency wallet. Think of it like the difference between keeping cash in your home safe versus a bank account.
- With a bank, the institution controls access to your money.
- With self-custody, you’re your own bank.
However, it comes with its own risks.
Banks’ shortfalls are one of the reasons why Bitcoin was invented in the first place, following the 2008 financial crisis that nearly bankrupted the world. Just look a bit more closely at Satoshi Nakamoto’s Bitcoin genesis block to see this for yourself.
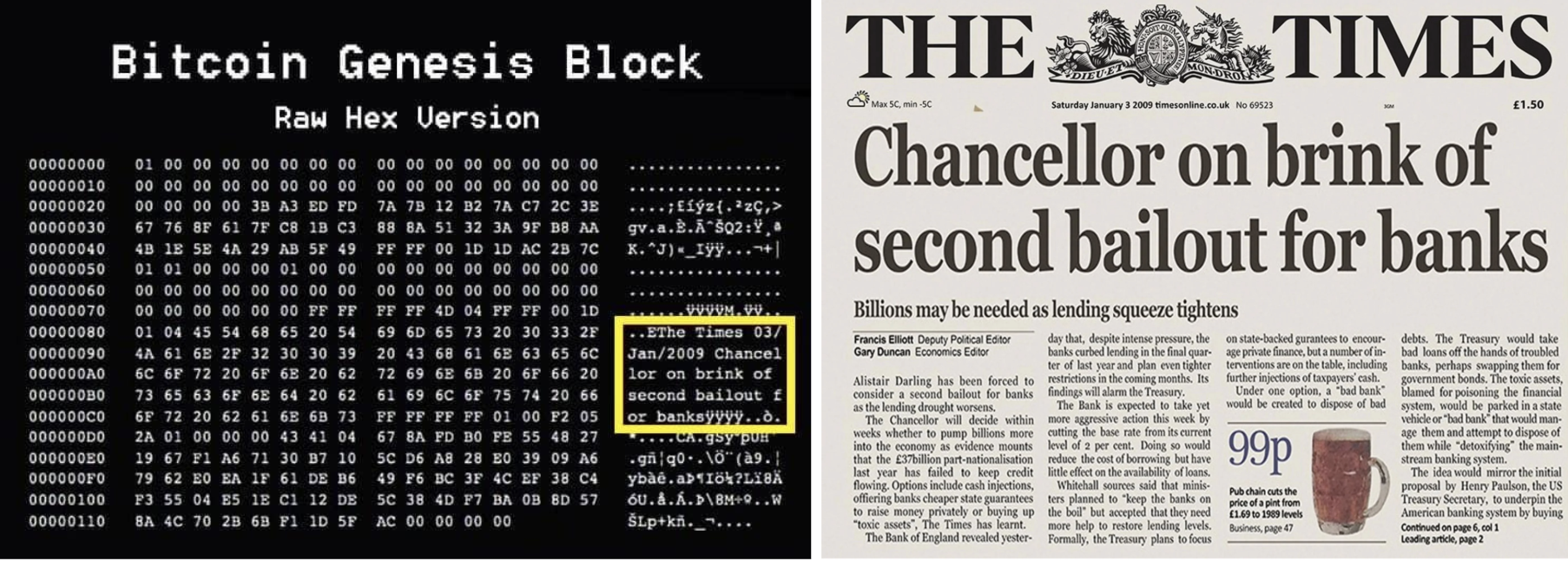
It directly references those nasty governments’ bailouts of banks as a warning of centralized finance’s limitations and overreach.
Self-custody is what crypto people mean when they shout out “Not your keys, not your coins”, and they’re not wrong.

Whoever controls the private keys or seed phrase of a wallet controls and thereby owns everything in it. Period.
While you can generally trust bluechip centralized exchanges (CEX) like Binance and Coinbase to safekeep the value of everyone’s holdings, it’s not as simple as that. There’s always a risk in crypto that something goes catastrophically wrong.
Don’t trust Proof of Reserves. Rather, trust Proof of Keys!
How Crypto Ownership Actually Works
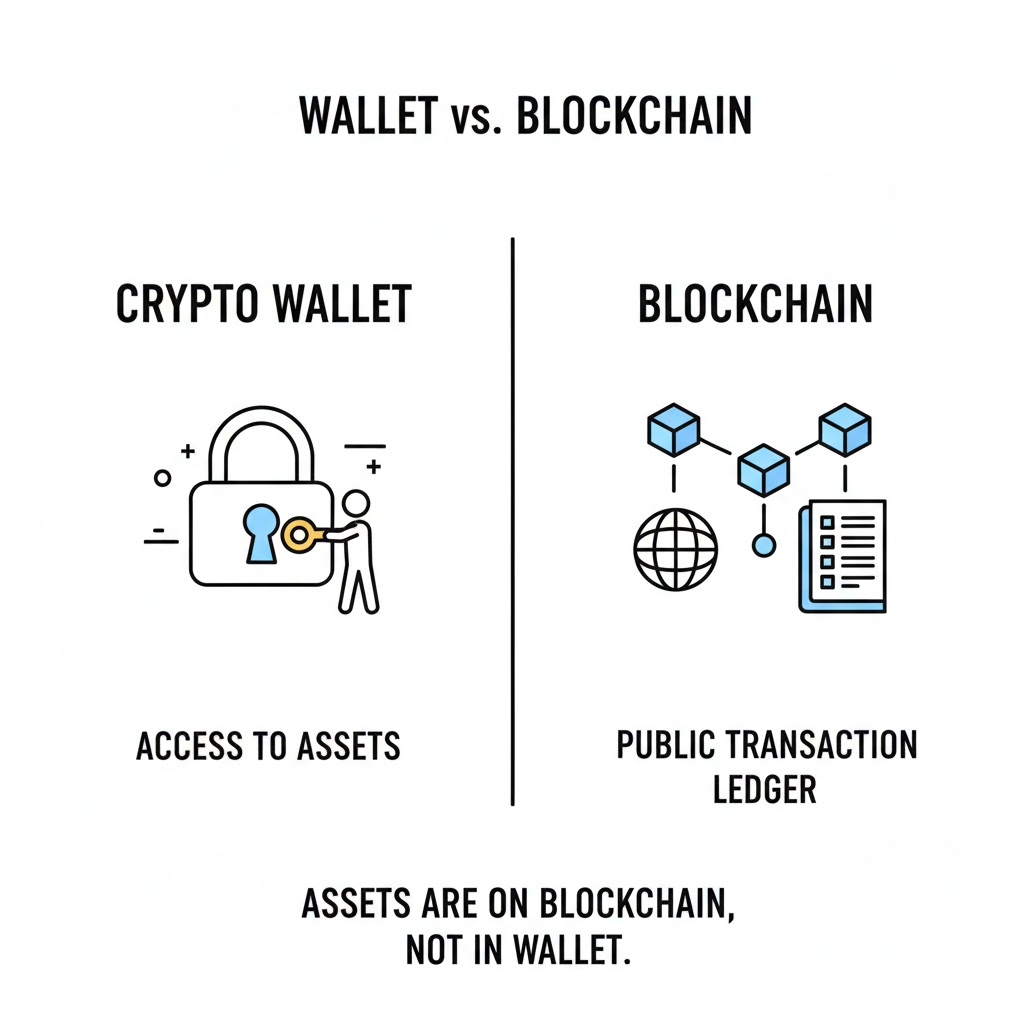
How does Crypto Work?
Here’s the first thing almost all crypto newbies get confused about:
Your cryptocurrency doesn’t live “in” a decentralized wallet like Phantom, Ledger or MetaMask. Your wallet is merely a software application that allows you, and only you, to access and control your holdings.
All crypto exists on “the blockchain”, a distributed network of connected computers that each maintain a complete copy of every transaction ever made on that network. Your Bitcoin, Ethereum or Solana coins never actually leave this public ledger, but can be transferred between its users.
What your private keys or recovery seed give you is direct access to them.
There are thousands of blockchains in existence now in 2026, and each have their own tokens, rules and specifications. However, they all need crypto wallets to reward their network participants with incentives to keep them loyal. These come in the form of a cryptocurrency.
What is a Crypto Wallet?
When we say you create a crypto wallet, what we actually mean is that you generate a pair of cryptographic keys, a public and a private key, which you can use to “sign” into your wallet application, much like a Google account, in order to send and receive your coins. However, there’s no backup party to bail you out, no “reset your password” feature. But more on that later.
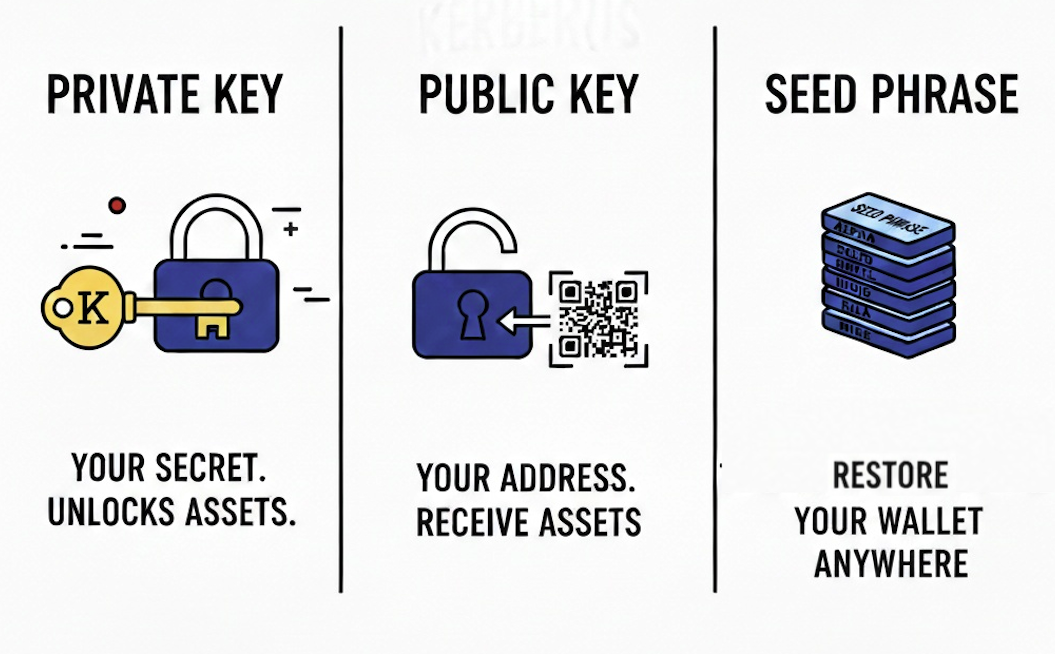
Public vs Private keys
This is where the cryptography bit comes in.
What is a Public Key?
Public keys work like your email address, you can share them with anyone to send you crypto.
You’ll usually be able to view them from inside your wallet application by clicking on the related “Receive” button, then copy and paste them where needed.
Warning: While it’s technically safe to expose your public key, it could open you to new security risks, especially if you “doxx” yourself (expose your real identity) and have a big portfolio, which anyone can view on websites like Etherscan or Solscan.
If they know who you are, criminals can target you through phishing campaigns, get you to copy and paste the wrong address when sending funds, or even attack you physically (the “wrench attack”). Only share your public key where necessary.
What is a Private Key?
Private keys are your password and proof of ownership. These let you access and spend your crypto. If someone gets access to your private key, they own your crypto now. Not “can access it” or “might steal it,” they own it. And they can take it whenever they want.
This is not like your Netflix password where you can just reset it and change your payment method. Your crypto wallet is software that stores these keys and helps you interact with the blockchain.
The wallet doesn’t contain your cryptocurrency, it contains the keys that prove you own specific amounts recorded on the blockchain.
I know, this conceptual distinction feels academic until you lose a phone and realize your crypto is actually fine because you have your seed phrase safely backed up with a hard copy at your grandma’s house.
What is a Seed Phrase?
Seed phrases are your own private key backup that’s easier to remember and record. They are also the most important part of the wallet creation process.
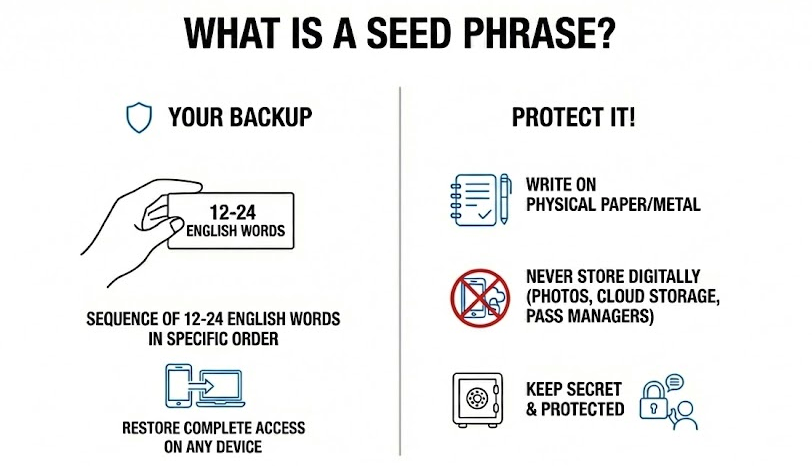
In short, a seed phrase is a sequence of 12 to 24 English words provided in a specific order that you need to write down. It allows you to restore complete access on a different device if you somehow lose access to your phone or computer.
These words must be:
- written on physical paper or metal, not stored digitally for safety reasons
- written in the correct order! Very important!
- not be recorded in photos, cloud storage, password managers (see LastPass’ $35m crypto breach), and certainly, no “encrypted notes app”
- Kept in secure, fireproof, waterproof locations
- Protected from anyone who might see them, including family members.
Remember: Getting one word wrong (let’s say lone instead of lane or line) or swapping their sequence by accident means you may not be able to recover your wallet. Ever.

Got it? Let’s review:
Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets
Custodial wallets are what exchanges like Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken give you.
- They hold your private keys.
- You get a username and password, but the exchange has ultimate control.
- If they freeze withdrawals, go bankrupt, or get hacked, you could lose access to your funds.
In most cases, you’ll have zero recourse except maybe getting in line with other bankruptcy creditors as we saw with FTX.
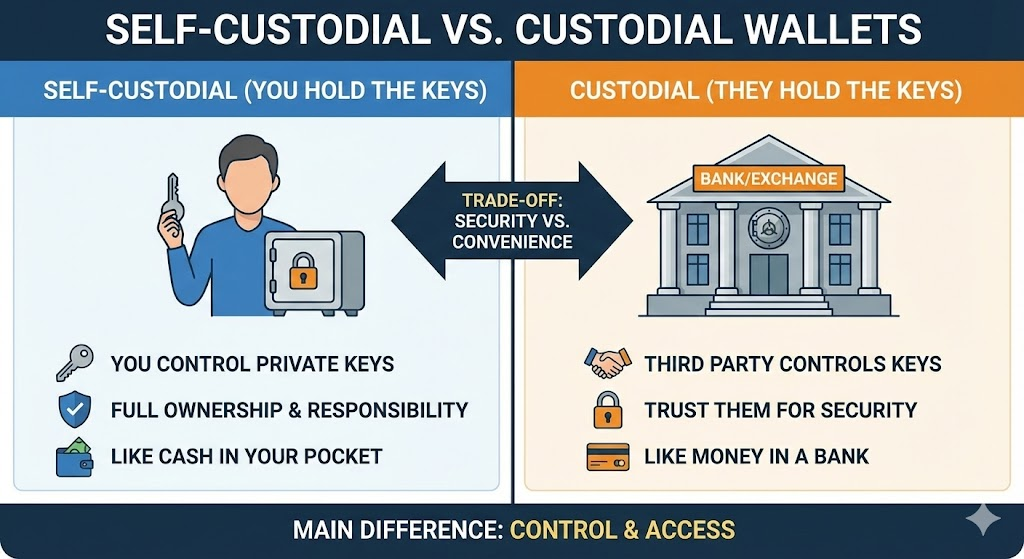
Like we explained earlier, self-custody (also called non-custodial) wallets put you in complete control.
- You generate and store your own private keys.
- No company can freeze your account.
- No exchange bankruptcy affects your holdings.
Downside? You’re entirely responsible for not screwing this up. On the upside, you’re in full control, 24/7.
Self-custody fundamentally changes your threat model. Instead of trusting an exchange like Kraken to protect $500 million in customer funds (making them a massive target), you only need to secure your own holdings. Your assets aren’t sitting in a giant honeypot with everyone else’s funds. Your security becomes very personal.
State-sponsored North Korean hackers aren’t targeting your personal Ledger. They’re targeting exchanges where one successful attack nets billions. Your personal wallet is basically invisible to organized hacking groups unless you’re holding genuinely life-changing amounts, and even then, physical security matters more than sophisticated attacks.
This is where modern tools actually help without undermining your control.
Kerberus: Securing Self-Custodial Wallets in Real-Time

Kerberus Sentinel3 is a sophisticated browser extension developed by cybersecurity veterans that employs automatic scam detection when you’re connecting your wallet to websites. Sentinel3 last year became the first Chrome extension ever to earn the VaaSBlock RMA badge.
Sentinel3 boasts a 99.9% detection rate across 1,000+ blockchain networks and blocks malicious sites before they reach your wallet, without ever touching your private keys. Kerberus also has an API for businesses looking to protect their users.
Install the Kerberus Sentinel3 extension here on Chrome Web Store
Why Self-Custody Matters in 2026
Real Asset Ownership and Financial Freedom
Self-custody delivers what cryptocurrency was designed to provide: actual ownership without needing anyone’s permission. When you control your private keys, no third party can freeze your withdrawals, close your account, or require three forms of ID and a video call to access your own money.
This sounds abstract until you try to withdraw $10,000 from Coinbase at 11 PM on a Sunday and get hit with “additional verification required” and a 72-hour hold. Then you get it.
It also doesn’t matter if the US or China bans Bitcoin or Ethereum. While it can crash the price and the blockchain itself might be deemed criminal for whatever reason, there’s no way to enforce its actual shutdown, thanks to its decentralized network of tens of thousands of computer nodes spread across the globe. You’d have to unplug the internet worldwide for that to happen.
Risky CEX Protection
The history of centralized exchanges is basically a horror movie franchise at this point:
- Mt. Gox (2014): 850,000 Bitcoin disappeared, worth $450 million then, over $50 billion today. Most users got pennies on the dollar years later, if anything.
- BlockFi (2022): Froze withdrawals and filed for bankruptcy because of FTX exposure. Customers are still fighting for their money.
- FTX (2022): Sam Bankman-Fried got 25 years in prison. Customers were locked out during a Bitcoin bull run. Solana went as low as $8.
- QuadrigaFX: CEO Gerald Cotton mysteriously died in India in 2018, taking with him over $215 million in investor funds in the process. There is still so much controversy over whether he’s dead and what really happened that it inspired a Netflix documentary.

According to Chainalysis:
- Over $2.2 billion was stolen in crypto hacks in 2024.
- That jumped to $3.4 billion in 2025.
And these are just the hacks we know about.
The Art of Crypto Self-Custody
Remember: You Are The Bank
First rule of self-custody: there’s no customer support hotline if you mess this up. No password reset button exists for lost private keys. No “I forgot my seed phrase” recovery flow.
Blockchain transactions are irreversible (“immutable”) by design. If you send funds to the wrong address, approve a malicious smart contract, or lose your private keys, your cryptocurrency is gone forever.
Not “might be recoverable,” gone. As in, those coins will sit on the blockchain until the implosion of the universe (or quantum computing?) because nobody can access them.
This is the trade-off for true ownership, and you need to make peace with it before moving serious money into self-custody.
Keep Private Keys Private
Private keys represent ultimate control.
Never enter them on websites. Never share them. Never ever leave a digital footprint.
This means: don’t store them on internet-connected devices. Don’t screenshot them because “I’ll delete it later,” you won’t, and that photo is now syncing to iCloud. Don’t even print them out.
Sounds Fishy? Don’t Get Phished

Phishing attacks remain the biggest Web3 security threat to self-custody. Why hack your wallet when a bad guy can trick you into giving access? Scammers create fake websites, social media accounts and emails that look identical to real crypto services, and they rely on psychological tricks to fool users.
One criminal in Brooklyn allegedly stole nearly $16 million just by impersonating Coinbase support and convincing people to “secure” their accounts by transferring funds to his wallet. Data breaches that exposed OpenSea and Ledger customer information led to them getting targeted by email accounts.
People fall for these scams because the sites look perfect and the timing is urgent. It’s all by design: stress and panic force people to make mistakes.
This is where tools like Kerberus Sentinel3 shine: it automatically detects and blocks these malicious sites, even brand new ones, in real-time, before you even connect your wallet.
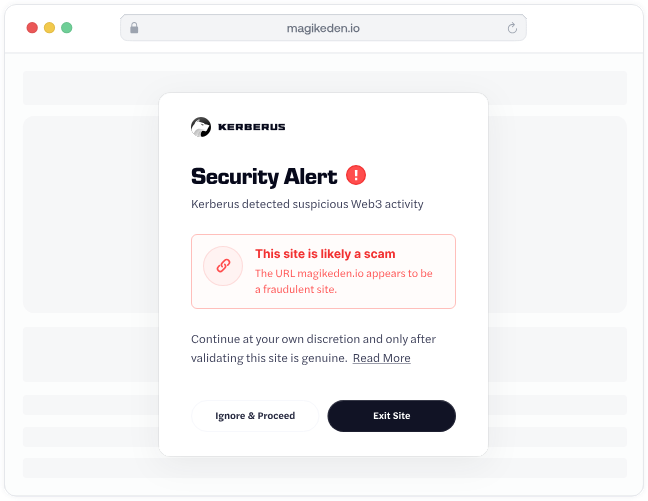
Sentinel3’s Social Shield extends this protection to social media platforms like X, where crypto folks good and bad live and breathe.
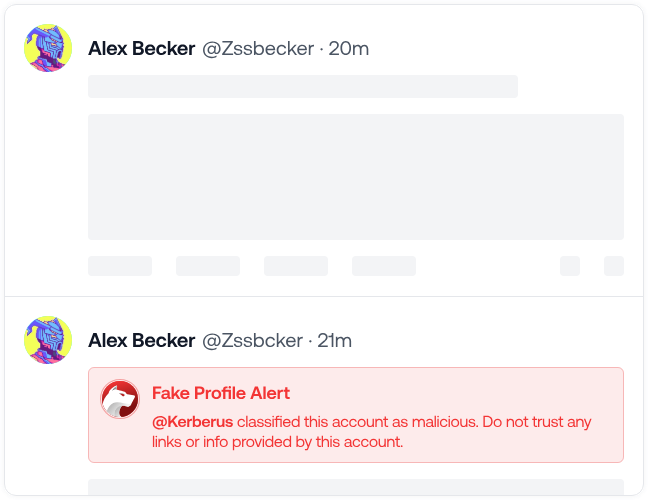
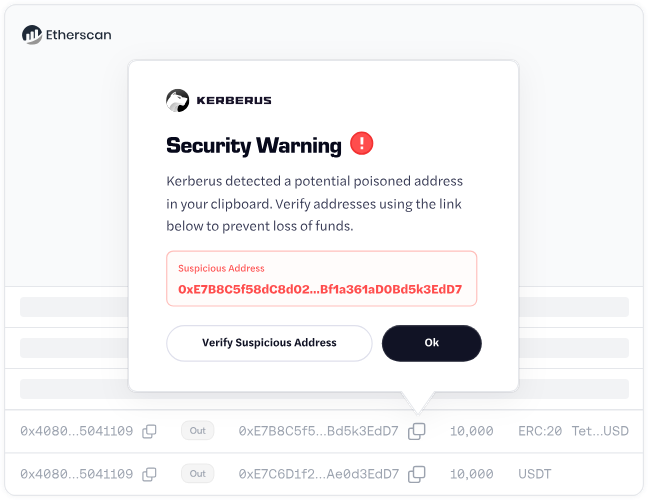
Address poisoning is as sneaky as it sounds. Attackers send you tiny amounts of crypto from addresses that look almost identical to ones you’ve used before. Like, the first 6 and last 6 characters match. You check your transaction history, copy what looks familiar, and boom, you just sent $50,000 to a scammer. Or $50 million, in the case of this poor guy in 2025.
Malware and wallet drainers are exactly what they sound like, malicious software that steals your crypto by secretly logging keystrokes, screenshotting everything, or just automatically approving transactions that empty your wallet.
Here are a few quick tips to stop them:
- Only download wallet software from official sources (verify the URL character by character)
- Keep your OS and security software updated
- Never enter seed phrases on internet-connected devices
- Use hardware wallets for anything over $5,000
Social engineering preys on human psychology.
Someone creates urgency (“Your account will be locked in 24 hours!”), impersonates authority (“This is Ledger support calling”), or offers something too good to be true (“Send 1 SOL, receive 2 SOL back!”).
Real companies never ask for your private keys or seed phrases. Not in emails. Not on phone calls. Not through Twitter DMs.
If someone asks, it’s a scam. They want your crypto. This is a universal rule with zero exceptions.
Hot vs Cold: Choosing Secure Wallet Types
Hot wallets (MetaMask, Trust Wallet) are software on your phone or computer. They’re convenient for frequent transactions but constantly exposed to malware and phishing. Use these for small amounts you actively trade or use, think of it as your spending money.
Cold wallets (Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T) are physical devices that store private keys offline. You connect them when you want to transact, approve on the device screen, then disconnect. They provide the strongest security for significant holdings.
The optimal setup combines both: hardware wallet for savings, hot wallet for pocket money. This is like keeping most money in a savings account while carrying $100 cash.
The Kerberus Advantage for Self-Custody
Self-custody gives you control over private keys, but it doesn’t protect you from clicking on the wrong website or approving a malicious smart contract. This is where Kerberus Sentinel3 becomes genuinely useful.
Traditional security relies on blocklists, databases of known scam websites. The problem? By the time a phishing site gets reported and added to the list, it’s already stolen from multiple victims. You’re hoping you’re not one of the first people to find a new scam site.
Kerberus uses AI-powered detection developed by offensive security veterans with 15+ years of experience. Instead of blocklists, the extension automatically identifies phishing sites from the moment they launch based on behavioral analysis and pattern recognition.
Sentinel3 never requests, accesses, or stores your private keys. It protects the connection layer without compromising your custody. Installation is literally one click, add the extension and it works automatically in the background.
This combination makes sense: you keep complete control (true self-custody) while adding professional-grade protection at the points where you’re most vulnerable.
Getting Started with Self-Custody
Step-by-Step for Beginners
- Start small. Begin with $50-100 you can afford to lose while learning. Mistakes happen—better with small amounts.
- Choose wisely. Complete beginners should use mobile wallets like Blue Wallet or Trust Wallet. Once comfortable, upgrade to hardware wallets (Ledger or Trezor) for holdings over $1,000.
- Secure your seed phrase immediately. Write down every word on paper during setup. Double-check each word. Store it in a fireproof safe before doing anything else.
- Practice first. Send $5 from an exchange to your wallet, then send $5 back. These test transactions confirm everything works.
- Add protection. Install Kerberus Sentinel3 for automatic threat blocking across 1,000+ chains. Zero configuration required.
Essential Security Practices
Seed phrase management:
- Write on physical materials only—never photograph or digitize
- Store copies in multiple secure locations (fireproof safe, bank deposit box)
- Test recovery with small amounts before trusting with real money
- Never enter seed phrases on websites—this is always a scam
Transaction security:
- Verify recipient addresses character by character
- Start with $10-20 test transactions to new addresses
- Be cautious with DeFi contracts that request token permissions
- Download wallet apps only from official sources
Hardware matters. For holdings over $10,000, hardware wallets are essential. They keep private keys offline and away from computer vulnerabilities.
Keep Learning. Self-custody requires ongoing education. Follow security researchers, understand transaction mechanics beyond basics, and stay informed about evolving threats. Never trust unsolicited DMs offering help.
Scale up gradually over 3-6 months. There’s no rush.
Conclusion
Self-custody is cryptocurrency’s original promise: actual ownership of digital assets without needing anyone’s permission. No exchange bankruptcy can freeze your funds. No company can impose arbitrary restrictions. No third party stands between you and your wealth.
This ownership requires real responsibility. You handle security that custodial services managed in the past for you. There’s a learning curve. Mistakes can be expensive. But, the trade-off is absolutely worth it.
Success with self-custody comes from starting small, following proven security practices, and using the best Web3 security tools that add protection without compromising your control.
Combining self-custody principles with real-time threat detection from Kerberus Sentinel3 gives you complete sovereignty while blocking the phishing sites, malicious contracts, and scams that target crypto users.
Ready for automatic scam protection? Install Kerberus Sentinel3 and get enterprise-grade security with zero setup. Join 250k+ users with zero losses, 99.9% detection rate, and up to $30,000 coverage per transaction.
Written by:
Werner Vermaak
Werner Vermaak is a Web3 author and crypto journalist with a strong interest in cybersecurity, DeFi, and emerging blockchain infrastructure. With more than eight years of industry experience creating over 1000 educational articles for leading Web3 teams, he produces clear, accurate, and actionable organic material for crypto users. His Kerberus articles help readers understand modern Web3 threats, real-world attack patterns, and practical safety practices in an accessible, research-backed way.
Read more about the authorRelated Guides
See more guides
How to Use Phantom Wallet Safely: A Beginner’s Guide
Feb 12, 2026 • 4 minutes read

Wake Up! WEF 2026 Cybersecurity Report Sounds Alarm For Crypto Sector
Feb 11, 2026 • 4 minutes read

Pig Butchering Romance Scams: How to Protect Your Crypto
Feb 8, 2026 • 4 minutes read

The Psychology of Crypto Scams: How And Why They Still Work
Jan 16, 2026 • 4 minutes read
Install once & immediately get protected from scams, phishing and hacks. Zero losses for 250k+ users in 3 years. Now with up to $30,000 in coverage.
