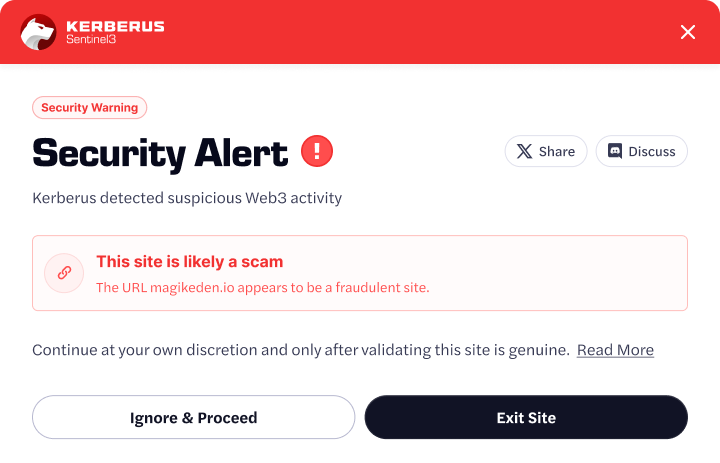
Front-End Compromise
Attackers hack dApp front-ends to steal your crypto. Learn how front-end compromises happen and how to verify websites with Kerberus.

What Is a Front-End Compromise?
A front-end compromise occurs when attackers infiltrate a decentralized application’s website or user interface to redirect users to malicious contracts or inject harmful code. Even if the underlying smart contracts are perfectly secure, a compromised interface can deceive users into signing transactions that drain their wallets or grant dangerous permissions. These attacks are particularly effective because users naturally trust interfaces they’ve used before, making malicious prompts nearly indistinguishable from legitimate ones.
How Front-End Compromises Work
Attackers exploit vulnerabilities through DNS hijacking where domain records are changed to point to malicious servers, JavaScript injection that modifies wallet connection flows or replaces contract addresses, compromised CDN resources that serve malicious code to all users, or social account takeovers that direct followers to counterfeit interfaces. They often perfectly mimic legitimate interfaces while replacing contract addresses with malicious ones or altering transaction parameters. The attack succeeds because the compromised front-end serves as the trusted interaction point between users and protocols.
DeFi example: The Curve Finance front-end compromise in 2022, where attackers hijacked the interface to steal $570,000 before being detected, demonstrates how quickly front-end attacks can drain funds when users trust familiar interfaces without verifying the underlying contract interactions
How to Reduce Risk
- Use a best-in-class Web3 security tool like the Kerberus browser extension to secure yourself pro-actively and get alerted before it’s too late.
- Verify website URLs carefully against official sources and bookmark legitimate platforms to avoid typosquatting domains
- Check contract addresses against official documentation before approving transactions, and use browser bookmarks rather than search results to access platforms and avoid address poisoning
- Monitor official project social channels for security announcements and verified domain information
Written by:
Werner Vermaak is a Web3 author and crypto journalist with a strong interest in cybersecurity, DeFi, and emerging blockchain infrastructure. With more than eight years of industry experience creating over 1000 educational articles for leading Web3 teams, he produces clear, accurate, and actionable organic material for crypto users.
- •8+ years in crypto & blockchain journalism
- •1000+ educational articles for leading Web3 teams
- •Former content lead at CoinMarketCap, Bybit, OKX
Related Terms
See more glossary termsInstall once & immediately get protected from scams, phishing and hacks. Zero losses for 250k+ users in 3 years. Now with up to $30,000 in coverage.